Comparing PVC Colorant Formats: Pigments, Pastes, Masterbatches
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of different colorant formats in PVC manufacturing to make informed decisions for quality, efficiency, and sustainability.
Different types of colorants used to color PVC
There are several types of colorants that can be used to color PVC, including pigments, masterbatches, and color concentrates. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when choosing a colorant for a specific application.
-
Dry Format (Pigments): Pigments in a dry powder form are one of the most basic ways to color PVC. They're composed of organic or inorganic materials that absorb certain wavelengths of light, giving them color. Pigments have high thermal stability, which is ideal for PVC processing. They are directly mixed into the PVC matrix during the compounding process. However, achieving a uniform and consistent color can be challenging with pigments due to issues with dispersion. The success largely depends on the mixing equipment and conditions. A downside is that they might require additional additives or surfactants to aid dispersion, and the process can be dusty.
-
Liquids (Pastes): These are pigments dispersed in a liquid carrier, often a plasticizer, which is compatible with PVC. The benefit of using pastes is the ease of mixing and better dispersion of pigments within the PVC matrix, leading to a more consistent color. Also, because the pigment is already well dispersed, the energy required during processing can be lower. However, it's important to consider that the liquid carrier can act as a plasticizer and affect the final properties of the PVC product, which may require reformulation of the PVC compound. Additionally, handling liquids can be messy and can potentially lead to waste if not managed properly.
-
Hybrid Carriers: Hybrid carriers refer to colorants which use a blend of polymeric and non-polymeric (often liquid) carriers. They offer a middle ground between pure polymeric carriers and liquid pastes, aiming to leverage the benefits of both. They can provide good dispersion, similar to liquids, but with less impact on the formulation as they can be designed to have similar rheological properties to the base resin. The balance can be tailored depending on the specific requirements of the application.
-
Polymeric Carriers (Masterbatches): These are highly concentrated colorants encapsulated in a thermoplastic carrier chosen to be compatible with PVC, like EVA or universal polymers. This carrier resin is colored by adding a high loading of pigments (typically around 20-50% by weight) and is then cooled and cut into a granular shape. The advantage of masterbatches is that they offer excellent dispersion of the colorant and they are easy to handle and dose in the manufacturing process. They have minimal impact on the physical properties of the PVC and are less dusty than dry pigments. However, they can be more expensive per unit of color due to the inclusion of the carrier resin, and they require precise dosing equipment to ensure color consistency.
-
Pre-Coloured Resin (Compound): In this case, the PVC resin itself is pre-colored during its manufacture. This method can provide the most consistent color and properties since every pellet of PVC is identical. However, the downside is that it's less flexible - if you want to change the color, you need to change the whole batch of resin, leading to potential wastage. It also requires a longer lead time to produce and can be more expensive due to the labor and resources involved in its production.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them will depend on factors such as the specific requirements of the end product, the capabilities and preferences of the manufacturer, and cost considerations. It's also worth noting that different methods might be combined or adapted to suit specific applications. For example, a masterbatch might be used to provide the base color for a PVC product, with additional pigments or additives added separately to achieve specific effects or properties.
How are pigments used when coloring PVC?
Pigments, are commonly used to color PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Pigments are insoluble solid particles that provide color to the PVC. Pigments are available in various colors and can be mixed to create a wide range of shades and hues.
Pigments are added to the PVC during the manufacturing process in a dry powder form. The pigments are mixed with the PVC resin and other additives, such as plasticizers and stabilizers, in a high-speed mixer. The mixing process disperses the pigments evenly throughout the PVC, creating a uniform color throughout the material.
Powder pigments are usually the cheapest option in terms of the initial purchase price. However, as stated above, pigments come with several disadvantages that can have a negative effect on the total cost of ownership.

to stand
out
How are masterbatches used when coloring PVC?
Masterbatches are a common way to color PVC. A masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of pigments or dyes dispersed in a carrier resin, such as PVC. The carrier resin serves as a carrier or vehicle for the pigment or dye, allowing it to be easily mixed into the PVC formulation during processing.Masterbatches are often used in PVC coloring because they offer several advantages over other coloring methods. These advantages include:
- Precise color control: Masterbatches can be formulated with precise concentrations of pigments or dyes to achieve specific colors or color shades.
- Ease of use: Masterbatches are easy to handle and can be added to the PVC formulation during processing with minimal additional processing steps.
- Cost-effectiveness: Masterbatches can be manufactured in high volumes, which can help to reduce the overall cost of coloring PVC.
- Consistency: Masterbatches are highly consistent and can help to ensure that the color of PVC is uniform across a batch.
- High color strength: they contain high levels of pigments or dyes, resulting in a highly concentrated and strong color.
- Flexibility: they can be customized to meet specific color requirements, allowing for a wide range of color options.
- Efficient use of materials: they are highly concentrated, allowing for the use of small amounts of colorant to achieve the desired color outcome.
- Consistency: they offer a high degree of consistency, ensuring that the color of PVC is uniform across a batch or production run.
- Cost-effective: Using color concentrates can be a cost-effective way to color PVC, as they allow for the efficient use of colorant materials and reduced processing time.
Masterbatches play an important role in coloring PVC by providing precise color control, ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and consistency. They are a popular choice for PVC coloring in many industries, including building and construction, automotive, and consumer goods.
Pigments vs Masterbatches such as Holcobatch
Powder pigments and masterbatches are both common methods of coloring PVC. However, there are some differences between the two:
- Concentration: Powder pigments are less concentrated than color concentrates. This means that larger quantities of powder pigments are needed to achieve the same color strength as a smaller amount of color concentrate.
- Dispersion: Powder pigments can be more difficult to disperse evenly throughout the PVC compound, which can result in inconsistent coloring. In contrast, color concentrates are specifically designed to be easily dispersed, leading to more consistent coloring.
- Handling: Handling and metering powder pigments can be more difficult and time-consuming than using pre-made color concentrates. Color concentrates can be added directly to the PVC compound, while powder pigments may need to be blended with a carrier resin before being added to the compound.
- Customization: Color concentrates can be easily customized to meet specific color requirements, whereas powder pigments are typically available only in standard colors.
- Cost: In some cases, powder pigments may be less expensive than color concentrates. However, the lower concentration and potential for uneven dispersion can result in higher overall costs due to the need for larger quantities and potential waste.
While powder pigments can be a cost-effective option for coloring PVC, they may also be more difficult to handle, less consistent, and less customizable than color concentrates. Masterbatches such as our proprietary Holcobatch, are a convenient and efficient option for coloring PVC with a high degree of consistency and customization options.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method
Both pigments and masterbatches are commonly used in the coloring of PVC pipes, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Pigments are finely ground powders or particles that are added to the PVC resin to produce a specific color. They are often used in relatively small amounts, typically around 1-5% by weight, and are typically added during the compounding stage of PVC processing. Pigments are highly customizable, and can be formulated to produce a wide range of colors and shades.
Masterbatches on the other hand, are pre-mixed blends of pigments and other additives, such as stabilizers, lubricants, or processing aids, that are added to the PVC resin in larger quantities, typically around 5-10% by weight. Masterbatches are often preferred in high-volume PVC processing operations, such as pipe extrusion, as they can help to streamline the production process and reduce the need for additional handling or processing steps.
One perceived advantage of pigments is that they tend to be less expensive upfront than masterbatches, which can be a factor in some applications. However, it's crucial to factor in the total cost of ownership.
Masterbatches on the other hand, offer several advantages in terms of processing efficiency and consistency. Because they are pre-mixed, they can help to ensure that the color is evenly distributed throughout the PVC resin, reducing the risk of color variation or streaking. They can also help to simplify the PVC processing operation, reducing the need for additional equipment or processing steps.
In the next segment, we will discuss the differences between Holcobatch, our proprietary product vs powder pigments with regards to handling and ease of use.
How do powder pigments compare to masterbatches with regards to in-line dosing?
In-line dosing is the process of adding colorants directly into the PVC melt stream during processing. In this context, masterbatches like Holcobatch, are typically preferred over powder pigments for in-line dosing due to their superior dispersion and easier handling.
Powder pigments can be more difficult to disperse evenly in the PVC melt, which can result in inconsistent coloring and lower quality end products. They may also require more processing time and higher shear rates to achieve proper dispersion, which can increase production costs.
On the other hand, masterbatches are specifically formulated for easy dispersion and consistent coloring. They are pre-dispersed blends of pigments, additives, and carrier resins that are designed to be added directly into the PVC melt stream during processing. This allows for more precise dosing and better control over the coloring process, resulting in higher quality end products.
While powder pigments can be effective for coloring PVC in certain applications, masterbatches are generally preferred for in-line dosing due to their superior dispersion, ease of handling, and consistent performance.
How do powder pigments compare to materbatches like Holcobatch with regards to cleaning?
Holcobatch is specifically engineered to overcome some of the challenges faced when using traditional powdered pigments in PVC coloring. It's a pelletized form of colorant with a hybrid carrier system that's compatible with PVC.
When it comes to the differences between Holcobatch and powdered pigments, several aspects are particularly noteworthy, especially in relation to cleaning:
-
Handling and Dispersion: Powdered pigments are often challenging to handle due to dust generation, which not only poses potential health risks but also creates a need for regular cleaning. These pigments require effective dispersion to achieve the desired color, which can be difficult. In contrast, Holcobatch comes in a pelletized form, which significantly reduces dust and hence the cleaning required. The pigments are already well dispersed in the carrier, ensuring a more uniform color upon processing.
-
Efficiency and Waste: The use of powdered pigments often leads to wastage due to poor dispersion and adherence to mixing equipment, which means more cleaning and potential loss of colorant. On the other hand, Holcobatch pellets are easier to handle, and the colorant is encapsulated in the carrier, which reduces wastage and the associated cleaning.
-
Equipment Wear: Powdered pigments, due to their abrasive nature, may contribute to equipment wear, leading to frequent maintenance and cleaning. Holcobatch, being in pellet form and having a softer carrier, would typically have less impact on the equipment, reducing the frequency of such cleaning and maintenance events.
-
Cleanup After Color Change: When changing colors, cleaning the processing equipment can be labor-intensive, especially with powdered pigments, where the dust can stick to many parts of the equipment. Since Holcobatch is in pellet form, it significantly reduces this issue, making color changeovers quicker and cleaner.
Holcobatch, due to its design and format, reduces many of the challenges associated with powdered pigments, particularly those related to cleaning. It offers a cleaner, more efficient, and user-friendly option for coloring PVC, making it an attractive choice for many manufacturers. Please note, the specific benefits may vary based on the particular formulation of Holcobatch and the exact processing conditions used.
Cleaner, typical dry pigment vs. Holcobatch
On the left you will see pigments. On the right, Holcobatch. The cleanliness is immediately visible. This also affects ease of handling, storage and of course, the wear and tear of the machine.
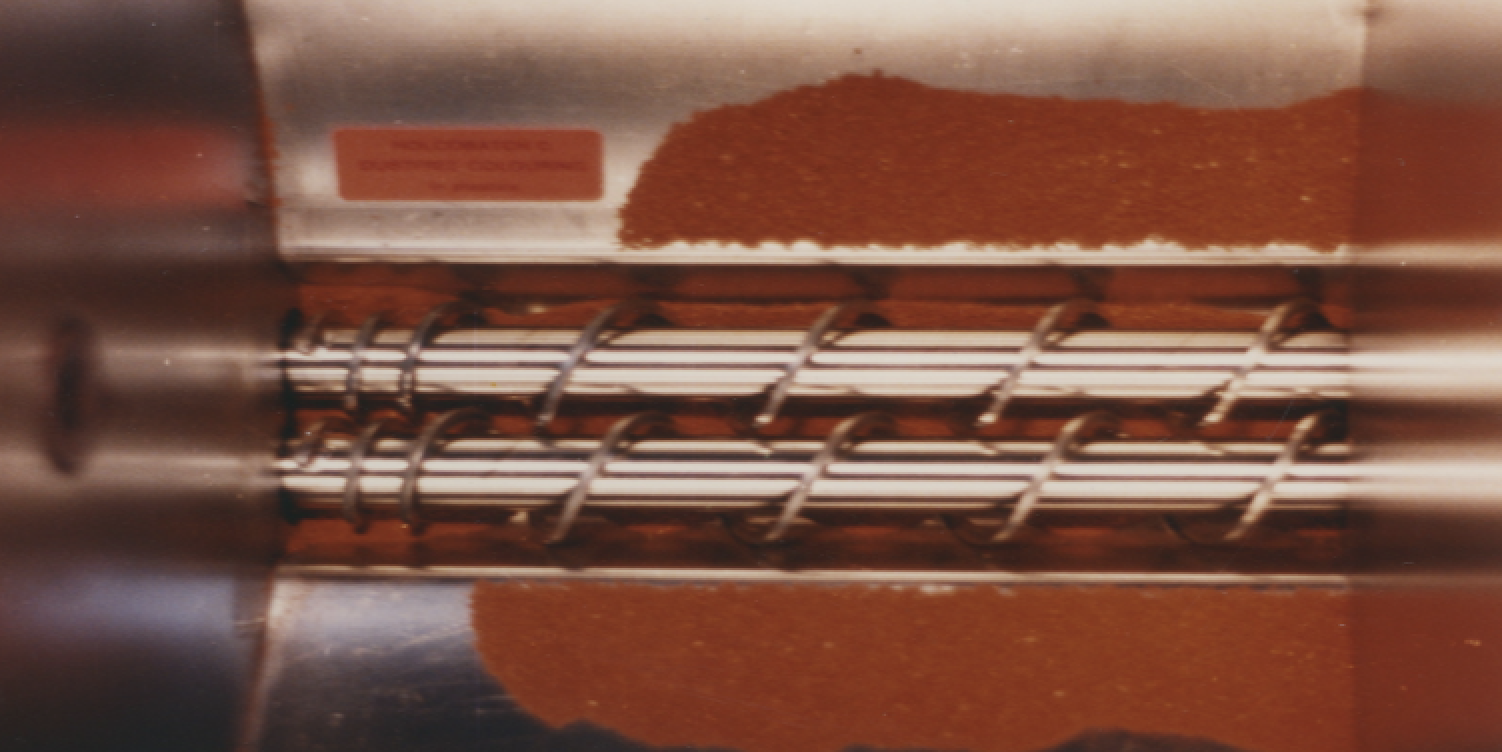
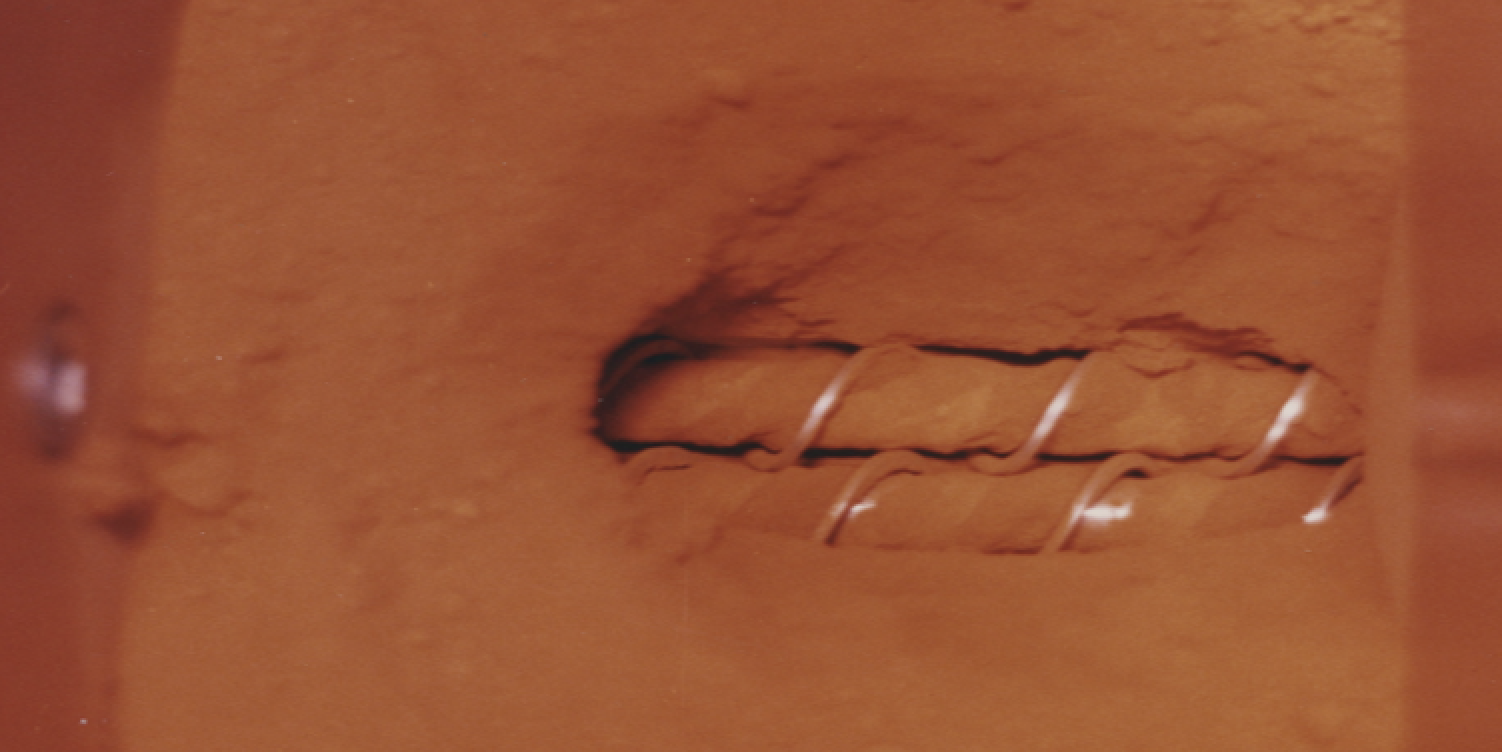
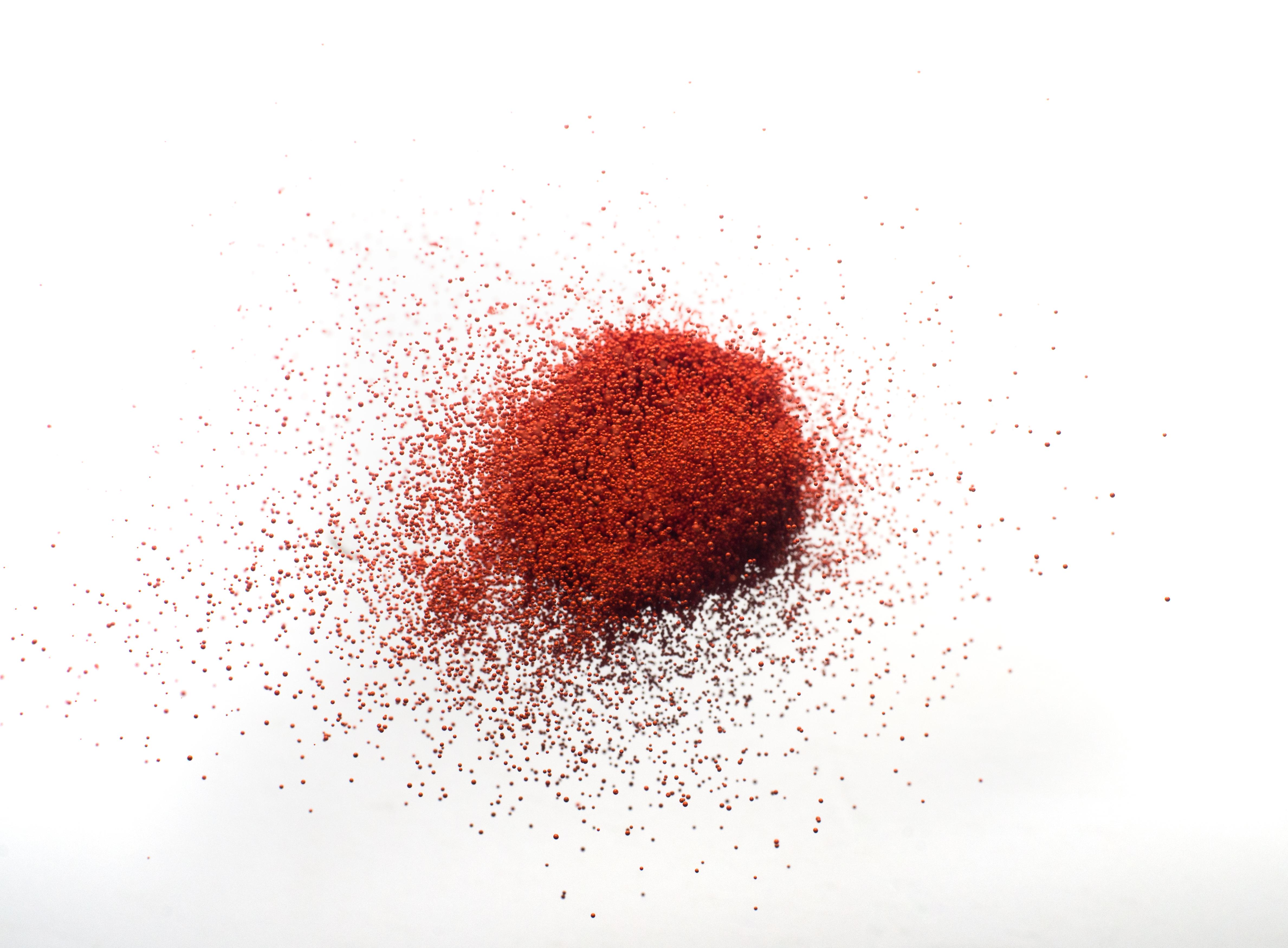
Highly concentrated, dust-free
Based on the experience of hundreds of companies across decades, we believe that Holcobatch is truly the best option for coloring PVC.
Holcobatch® was created in 1979 and was the first colorant product to encapsulate pigments and additives using a renewably sourced product instead of a polymer. This was unique at the time – and it remains so today, making Holcobatch® a truly sustainable colorant.
Holcobatch® is also highly pigmented and offers excellent coloring consistency. Thanks to its unique composition, it has a lower melting point than the alternatives. This enables quick color release, resulting in optimal distribution of the colorant. This means it can be used in low doses, which is another win for the environment.
Used in: Flooring, insulation, pipes and fittings, profiles, sheets, siding and cladding.

to stand
out
